B12
Vitamin B12 Supplement for Wellness
What is ‘Improved Wellness’?
In relation to Vitamin B12, this is seen as an improvement on
a persons’ general energy levels, mood, quality of sleep and
feelings of wellbeing: via a treatment plan consisting of IM
Injections of Hydroxocobalamin, dietary guidance and supplementation.
Anecdotal evidence of six years of the author administering
Vitamin B12 injections suggests that patients’ report a wealth
of benefits from treatment. These include, (but not limited to)
more physical energy, mental alertness and stamina for everyday
tasks, improved sleeping patterns, feeling emotionally
brighter/happier, better short-term memory, finding it easier
to exercise and lose weight, less frequency in urination and
improved bladder continence. Generally, an all round feeling of
“improved wellness”.


What is Vitamin B12 & Why do we need it?
An essential micronutrient, so called because the body cannot
synthesise this vitamin, and therefore we must either have it in our diet
or supplement our diet with it.
Deficiency of B12 or folate deficiency anaemia, can cause symptoms of
fatigue, pallor, heart palpitations and breathlessness. Specific to
pernicious (megaloblastic) anaemia, additional symptoms may include
depression, mouth ulcers, and pins & needles.
Vitamin B12 supplementation is reportedly safe and without common side-effects, however prompt treatment is required to reverse extensive deficiency, before it becomes irreversible.
The main causes of Vitamin B12 Deficiency
1) Malabsorption of food cobalamin:
“Food-cobalamin malabsorption is marked by the inability to release cobalamin from food, which therefore cannot be taken up by intrinsic factor for absorption. Release of cobalamin from food requires acid and pepsin, and most food-cobalamin malabsorptive states can be traced to gastric defects.
However, other mechanisms may also play a role” (Carmel 1995, Shipton, 2015). Certain medications affect the production of gastric acid and pepsin and will be identified on consultation/patient assessment. Conditions of the small intestine (e.g: Crohn’s disease, coeliac disease), parasites or bacterial growth may also lead to deficiency, along with conditions such as atrophic gastritis, alcohol misuse, pernicious anaemia and immune system disorders (e.g: Graves’ disease, Lupus).
2) A diet lacking in essential B vitamins:
More commonly seen than in previous years, owing largely to the rise in numbers of vegans/vegetarians. Also prevalent in patients who follow ‘fad diets’, macrobiotic diets, or other restrictive diets, that fall short of dietary recommendations, or people wo generally eat a very poor diet for a long period of time.
3) Aging:
NHS UK states that both Vitamin B12 deficiency and folate
deficiency are more common in older people, affecting around
1 in 10 people over 75 yrs and 1 in 10 people aged 65 – 74 yrs.BODY
Who is most at risk & most suitable for
B12 injections?
• Vegans/Vegetarians, people following restrictive diets.
• Alcoholics.
• People suffering from persistent stress.
• The elderly: As we age, the ability to digest and absorb Vitamin B12 may decrease. Between 15-40% of people over 60 have low serum B12 levels (Pacholok & Stuart, 2011).
• People with a Medical or Surgical History of bariatric surgery or who have had part of their intestines removed, as well as those with absorptive disorders like inflammatory
bowel disease, and those with duodenal ulcers.
Also persistent diarrhoea sufferers.
• People taking certain medications

Biotin

What is Biotin?
Biotin is a B-complex vitamin, also known as B7 or Vitamin H. Biotin is necessary for the cell growth and the production of fatty acids in living organisms. Biotin converts fatty acids and
glucose into fuel to produce energy. It helps to produce enzymes by metabolizing amino acids and carbohydrates.
• Biotin is a form of vitamin B found in foods including eggs, legumes, nuts, seeds, beef liver, sweet potatoes, mushrooms, bananas, broccoli, yeast and avocados.
• Biotin supplementation can be via oral medication or intramuscular injection.
• Biotin intramuscular injections can be for hair growth and strengthening, also to aid in the health of sweat glands.
• Improved health of nerve tissue and bone marrow.
• Improves acne and eczema.
• Strengthens hair and nails.
• Aids in preventing hair loss.
• Increases metabolism and speeds up weight loss.
• Improves blood glucose.

How can Biotin benefit beauty?
Research suggests that the vitamin ‘Biotin’ improves the basic protein ‘keratin’, that makes up hair, skin and nails. For the purposes of this course, intramuscular injections are suggested as increasing biotin levels more rapidly, to increase hair growth, hair structure and thickness, as well as decrease hair loss.
Prevention of grey hair, biotin protects the natural hair pigmentation prevents premature greying.
Nail growth: via the stimulation of proteins can reduce nail splitting and brittle nails. Oral biotin has been reported to be successful in the treatment of brittle nails. The mechanism by which it increases the matrix mitotic rate is unclear, but studies in vitro showed that biotin stimulates epidermal cell differentiation and aids in maintaining epidermal cell growth, which may help to improve NGR. Furthermore, biotin plays a
role in increasing the thickness of the nail plate.s2
In a study that evaluated patients with brittle nail syndrome, there was a 25% increase in nail
thickness after oral 2.5 mg biotin over six months.s3
(Garbers et al, 2021)
How can Biotin benefit general health?
• Diabetes – Biotin helps regulate blood sugar levels.
• Fertility – is boosted by adequate levels of Biotin.
• Heart Health – the prevention of heart disease by the lowering of blood pressure/ reduction in cholesterol levels/reduction in triglycerides in the body/ all as a result of elevated Biotin levels.
• Joint Pain – reduced inflammation in the joints enables a reduction in joint pain.
• Regulation of the menstrual cycle.
• Wound Healing is assisted by Biotin.

Vitamin D
Vitamin D and Wellness
It’s a simple concept, we get vitamin D from the sun, and in the U.K, we are not exactly blessed with much sunshine from September to March. Therefore, it stands to reason that we would need to look at other sources of it.
There is a proposed multitude of benefits from vitamin D, and some are very commonly documented (such as reduced incidence of colds and flu); which now includes the most recent summation that vitamin D may play a role in the prevention of Covid-19.
Benefits are not limited to physical health; studies on vitamin D regulating mood and a decrease in negative emotions have been shown as significant. Part of everyday wellness is the promotion of our mental well-being, just as much as our physical wellness.
Overall the prevention and treatment of many diseases and health conditions is an appealing reason to supplement with oral or IM injection of vitamin D.


Vitamin D is a pro-hormone which means it is present/ utilised by every cell in our bodies.
Vitamin D is imperative in the absorption of calcium and phosphate; which in turn are responsible for the presentation of healthy teeth, muscles and bones.
It is often described as a ‘key nutrient’ in maintaining heart health and essential for a balanced mood. Undisputed clinical research finds it provides an immune system function, which in light of the recent coronavirus pandemic, has reignited the public’s interest in it.
Together with the ever-increasing amount of knowledge and health education available; the public are now demanding more options for overall wellness and nutrition.

Who is at Risk
of Vitamin D deficiency
People with conditions that limit fat absorption:
Because vitamin D is fat soluble, its absorption depends on the
gut’s ability to absorb dietary fat . Fat malabsorption is
associated with medical conditions that include some forms of
liver disease, cystic fibrosis, celiac disease, Crohn’s disease, and
ulcerative colitis. In addition to having an increased risk of
vitamin D deficiency, people with these conditions might not eat
certain foods, such as dairy products (many of which are fortified
with vitamin D) or eat only small amounts of these foods.
Individuals who have difficulty absorbing dietary fat might
therefore require vitamin D supplementation.
Vegetarians and Vegans:
People following a plant-based diet, as a lot of food that naturally
has vitamin D is fish, red meat, and eggs
People who are obese or have undergone gastric bypass surgery:
Individuals with a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or more have lower serum 25(OH)D levels than non-obese individuals.
Obesity does not affect the skin’s capacity to synthesize vitamin D. However, greater amounts of subcutaneous fat sequester more of the vitamin. Obese people might need greater intakes of vitamin D to achieve 25(OH)D levels like those of people with normal weight.
Obese individuals who have undergone gastric bypass surgery
can also become vitamin D deficient.
Symptoms
of Vitamin D Deficiency
- Excessive sweating
- Constant tiredness/unusual fatigue
- Aching bones
- Cuts and
bruises take
forever to
heal
- Muscle pain
& soreness for
prolonged
periods
- Hair falling
out more
than usual
- Chronic pain in the body
(fibromyalgia)
- Unusual amount of hair loss
- Frequent sickness – repeated viruses like colds & flu
- Depression/feeling very sad
Vitamin C

Functions of Vitamin C:
Vitamin C, also known as ascorbic acid, has several important functions.
These include:
•Helping to protect cells and keeping them healthy
•Maintaining healthy skin, blood vessels, bones and cartilage
•Helping with wound healing
(NHS.co.uk)

Health Benefits of Vitamin C:
Stress:
Alcoholics, smokers and obese patients have been shown to be deficient in vitamin C. These types of stress-related diseases are linked to depleted nutrients, and lower levels of vitamin C.
Stroke:
A higher concentration of vitamin C in the blood was associated with 42% less risk of having a stroke, compared with individuals with the lowest concentrations, in a study in the American Journal of Public Health.

Colds and Flu:
There is no clinical evidence that vitamin C cures the common cold, however it is well documented that it can be beneficial in reducing the risk of complications such as pneumonia and lung infections.
More….
Other documented studies
suggest that vitamin C may be
beneficial in:
- Reducing inflammation
- Lowering the risk of cancer and cardiovascular disease
- Improving macular degeneration

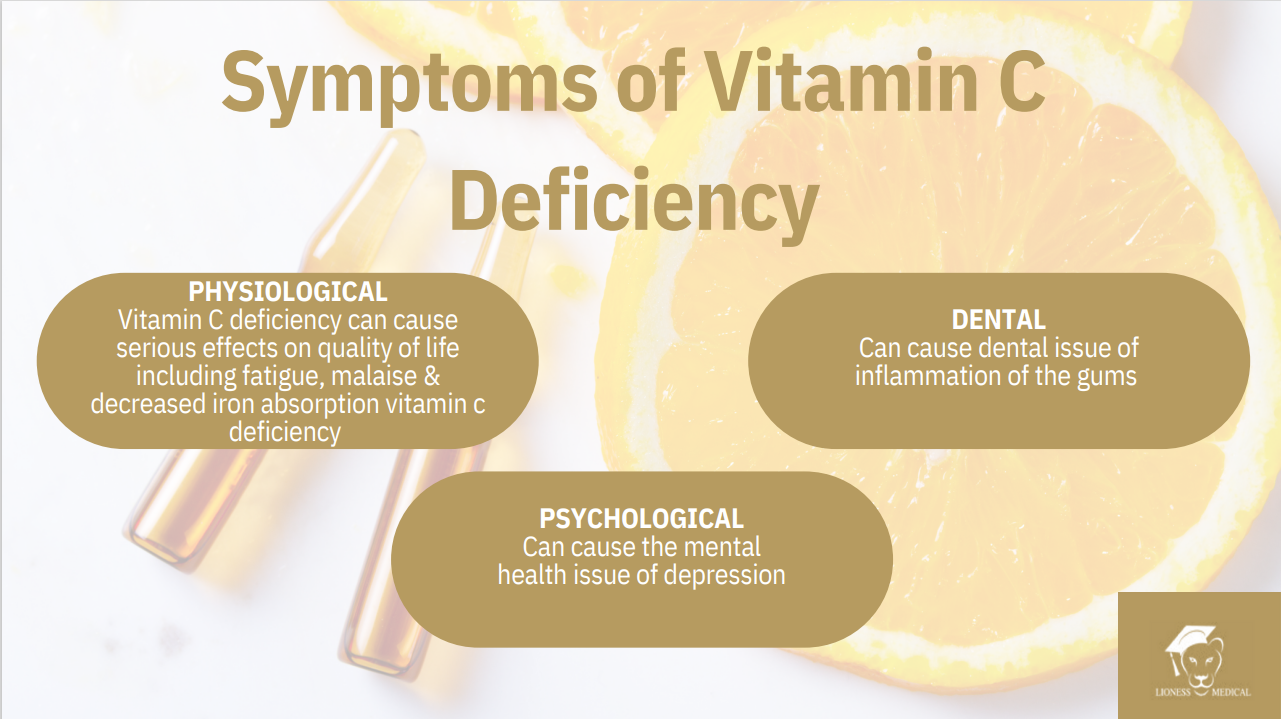
Symptoms of Vitamin C
deficiency:
- Anaemia
- Infections
- Scurvy
- Poor wound healing & bruising easily capillary haemorrhage
- Muscle degeneration

Recognising Vitamin C Deficiency:
- Atherosclerotic plaques
- Neurotic disturbances
- Irritability and sadness
- Severe joint or leg pain
- Swollen, bleeding gums
- Rough, dry, bumpy skin
- Slow wound
healing
- Persistent iron
deficiency, anaemia
- Corkscrew shaped body hair
- Painful, swollen joints
- Fatigue & low mood
- Bright red hair follicles
- Weakness in the bones
- Unexplained weight gain
- Bleeding gums and tooth loss
- Spoon shaped fingernails with red spots or lines
- Chronic inflammation and oxidative stress
- Easily bruised
- Poor immunity
Who is at Risk
of Vitamin C deficiency
- Smokers and passive smokers: lower plasma & leukocyte levels than non-smokers.
- Malabsorption–patients who have difficulty in the digestion or absorption of nutrients from food. This can include patients who have illnesses or conditions that cause chronic diarrhoea or abnormal stools (Irritable bowel syndrome, inflammatory bowel disease e.g.: Chrons or ulcerative colitis, celiac disease, poor diet, those on weight-loss programs, and those with excessive gas.)
- Furthermore, patients with severe infections, endocrine disorders, and those who have food sensitivity or allergies may also suffer malabsorption. Lastly, some medications may cause this to be exacerbated, these include neomycin,
cholestyramine, ant-acids, laxatives, paraminosal-icylic acid, colchicine and oral hypoglycaemic agents (biguanides e.g. Metformin & Phenformin).
- Patients with cancer & end stage renal disease, and chronic haemodialysis (Patients undergoing chemotherapy or radiation should consult with their oncologist prior to having this treatment).











